中间件顾名思义,是介于request与response处理之间的一道处理过程,相对比较轻量级,并且在全局上改变django的输入与输出。因为改变的是全局,所以需要谨慎实用,用不好会影响到性能。
如果你想修改请求,例如被传送到view中的**HttpRequest**对象。 或者你想修改view返回的**HttpResponse**对象,这些都可以通过中间件来实现。
可能你还想在view执行之前做一些操作,这种情况就可以用 middleware来实现。
Django默认的Middleware:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
|
自定义中间件
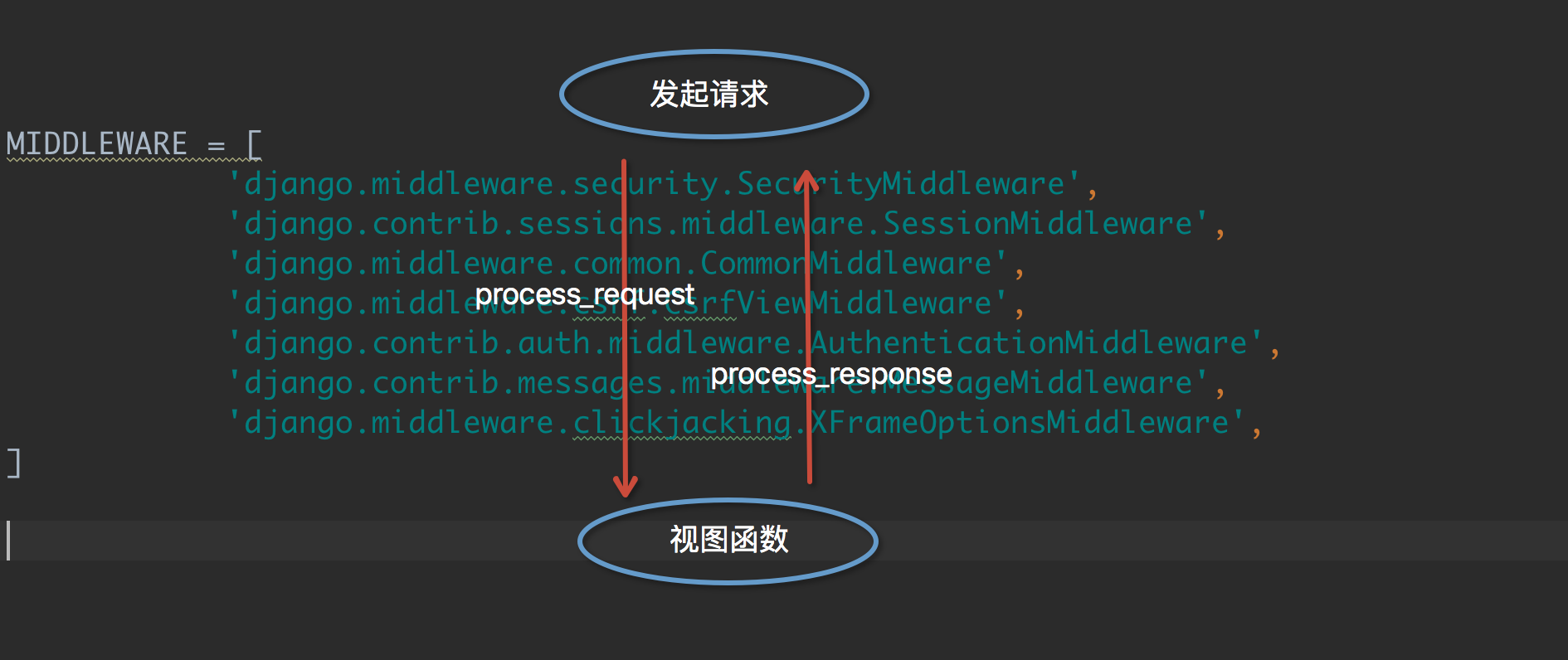
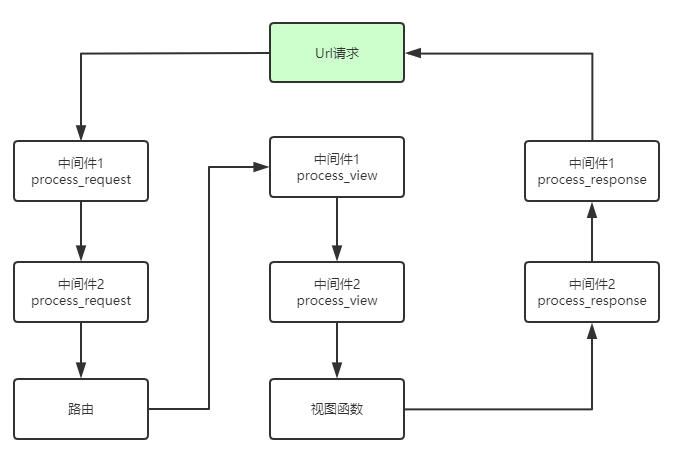
中间件一共有4个方法:process_request,process_view,process_exception,process_response。
process_request,process_response
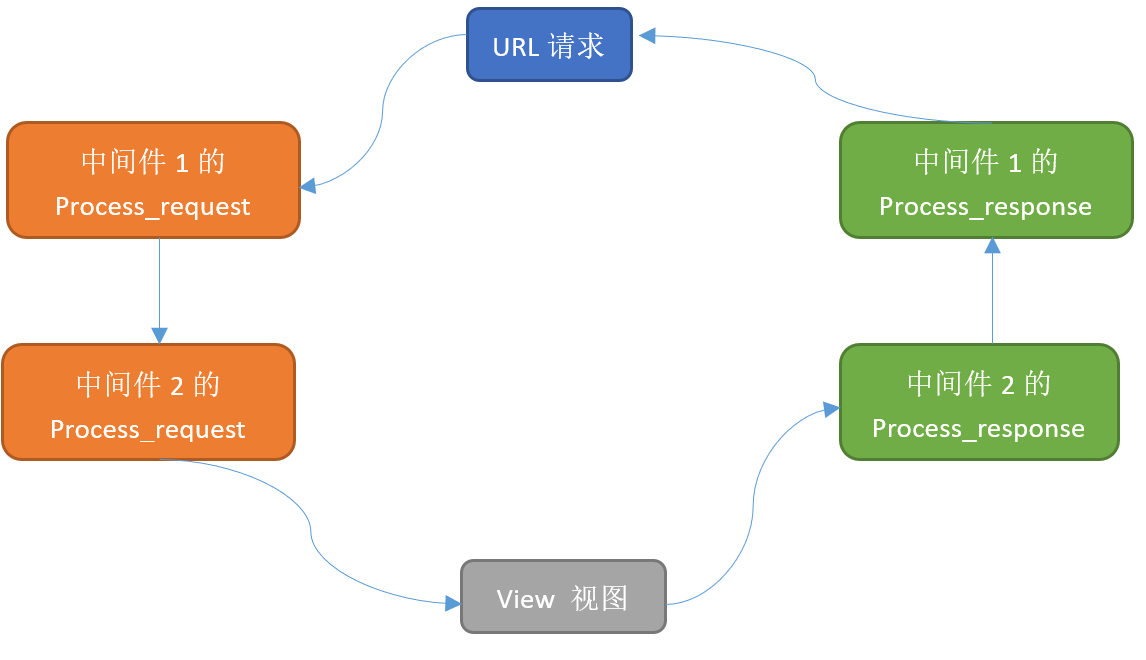
当用户发起请求的时候会依次经过所有的的中间件,这个时候的请求从process_request,最后到达views的函数中,views函数处理后,在依次穿过中间件,这个时候是process_response,最后返回给请求者。
![img]()
上述截图中的中间件都是django中的,我们也可以自己定义一个中间件,我们可以自己写一个类,但是必须继承MiddlewareMixin
需要导入
1
2
|
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
|
![img]()
定义视图
1
2
3
4
5
| from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
def index(request):
print('我是index视图')
return HttpResponse('ddd')
|
定义中间件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/4/26 16:32
# @Author : Tony Yu
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
class Test1Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试1中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试1中间件响应')
return response
class Test2Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试2中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试2中间件响应')
return response
|
测试
访问index视图路由,打印结果:
1
2
3
4
5
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是index视图
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
流程
![img]()
提前中断
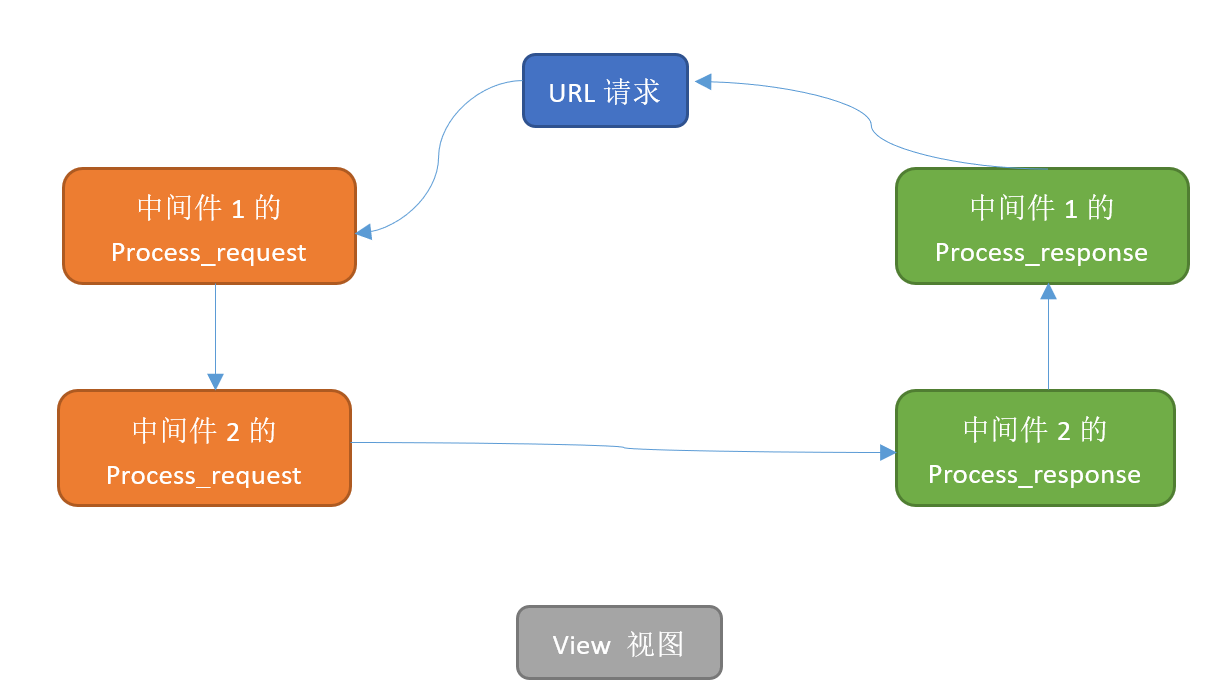
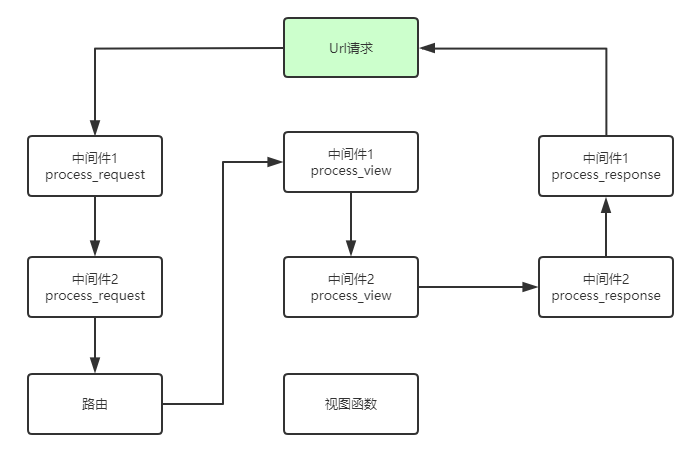
如果当请求到达请求2的时候直接不符合条件返回,即return HttpResponse("Md2中断"),程序将把请求直接发给中间件2返回,然后依次返回到请求者,中间件如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/4/26 16:32
# @Author : Tony Yu
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
class Test1Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试1中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试1中间件响应')
return response
class Test2Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试2中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
return HttpResponse('我是测试2中间件中断')
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试2中间件响应')
return response
|
运行结果:
1
2
3
4
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
可以看到直接跳过了我们原来的视图函数,流程编程了如下:
![img]()
process_view
1
| process_view(``self``, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs)
|
该方法有四个参数
request是HttpRequest对象。
callback是Django即将使用的视图函数。 (它是实际的函数对象,而不是函数的名称作为字符串。)
callback_args是将传递给视图的位置参数的列表(无名分组分过来的值).
callback_kwargs是将传递给视图的关键字参数的字典(有名分组分过来的值)。 callback_args和callback_kwargs都不包含第一个视图参数(request)。
Django会在调用视图函数之前调用process_view方法。
它应该返回None或一个HttpResponse对象。 如果返回None,Django将继续处理这个请求,执行任何其他中间件的process_view方法,然后在执行相应的视图。 如果它返回一个HttpResponse对象,Django不会调用适当的视图函数。 它将执行中间件的process_response方法并将应用到该HttpResponse并返回结果。
定义中间件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/4/26 16:32
# @Author : Tony Yu
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
class Test1Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试1中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试1中间件响应')
return response
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试1中间件的process_view')
class Test2Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试2中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试2中间件响应')
return response
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试2中间件的process_view')
|
运行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试1中间件的process_view
我是测试2中间件的process_view
我是index视图
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
流程
![img]()
提前中断
如果当请求到达process_view2的时候直接不符合条件返回,即return HttpResponse("Md2中断"),程序将把请求直接发给中间件2返回,然后依次返回到请求者,中间件如下:
即:中间件代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/4/26 16:32
# @Author : Tony Yu
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
class Test1Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试1中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试1中间件的process_view')
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试1中间件响应')
return response
class Test2Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试2中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试2中间件的process_view')
return HttpResponse('测试2中间件的process_view中断你')
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试2中间件响应')
return response
|
输出结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试1中间件的process_view
我是测试2中间件的process_view
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
此时流程变为:
![img]()
直接跳过视图函数了
注意:process_view如果有返回值,会越过其他的process_view以及视图函数,但是所有的process_response都还会执行。
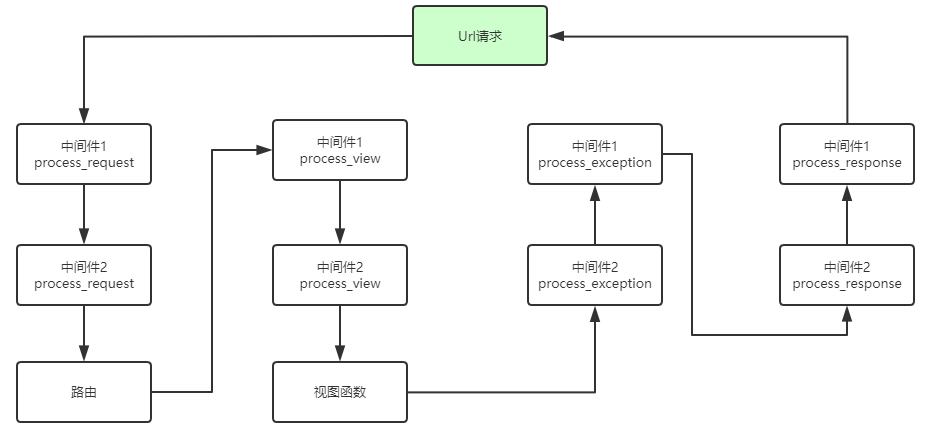
process_exception
1
| process_exception(self, request, exception)
|
该方法两个参数:
一个HttpRequest对象
一个exception是视图函数异常产生的Exception对象。
这个方法只有在视图函数中出现异常了才执行,它返回的值可以是一个None也可以是一个HttpResponse对象。如果是HttpResponse对象,Django将调用模板和中间件中的process_response方法,并返回给浏览器,否则将默认处理异常。如果返回一个None,则交给下一个中间件的process_exception方法来处理异常。它的执行顺序也是按照中间件注册顺序的倒序执行。
定义中间件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/4/26 16:32
# @Author : Tony Yu
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
class Test1Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试1中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试1中间件的process_view')
def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('我是测试1中间件的process_exception', exception)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试1中间件响应')
return response
class Test2Middleware(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('我是测试2中间件请求', request.method, request.path)
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('我是测试2中间件的process_view')
def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('我是测试2中间件的process_exception', exception)
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('我是测试2中间件响应')
return response
|
运行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试1中间件的process_view
我是测试2中间件的process_view
我是index视图
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
我们发现process_exception并没有执行,上面说过,只有视图函数出错他才会运行,此时流程为:
![img]()
视图出错
视图函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
def index(request):
print('我是index视图')
raise ValueError('报错吧')
return HttpResponse('ddd')
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 我是测试1中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试2中间件请求 GET /wechat/index/
我是测试1中间件的process_view
我是测试2中间件的process_view
我是index视图
我是测试2中间件的process_exception 我是index视图,我出错了
我是测试1中间件的process_exception 我是index视图,我出错了
我是测试2中间件响应
我是测试1中间件响应
|
![img]()
运行流程
![img]()
应用场景
做IP访问频率限制
URL访问过滤(没登陆就要登陆才能访问)
如果用户访问login则放过,其他也没检测是不是有session,已经有了放过,没有放回login
Django项目中默认启用了csrf保护,每次请求时通过CSRF中间件检查请求中是否有正确token值
Django默认的CSRF中间件将拦截写到了process_view中,这样做是可以过滤请求方法带的有装饰器。
默认的csrf中间件拦截全部,如果某个请求中我们不需要,可以使用自带的装饰器
fbv下取消拦截
1
2
3
| from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
def test(request):
return ...
|
cbv下取消拦截
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
class TestView(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse('我是get')
def post(self, request):
return HttpResponse('我是post')
|
路由取消拦截
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| from django.conf.urls import url
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^myview/$', csrf_exempt(views.MyView.as_view()), name='myview'),
]
|
单独拦截的装饰器
用法和取消拦截的一样
1
| from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_protect
|
当有用户请求过来时,判断用户是否在白名单或者在黑名单里